- 2011 — 28nm GCN 1.0 — Tahiti / Cape Verde
- 2013 — 28nm GCN 2.0 — Hawaii / Bonaire
- 2015 — 28nm GCN 3.0 — Fiji / Tonga
- 2016 — 14/16nm FinFET Polaris (GCN 4.0)
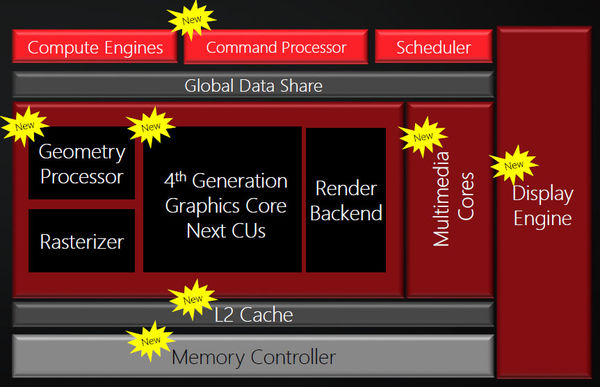
The GPU design was modified to include new logical blocks. What’s new is Command Processor, Geometry Processor, Multimedia Cores, Display Engine and upgraded L2 Cache and Memory Controller.

AMD’s Polaris architecture-based 14nm FinFET GPUs deliver a remarkable generational jump in power efficiency. Polaris-based GPUs are designed for fluid frame rates in graphics, gaming, VR and multimedia applications running on compelling small form-factor thin and light computer designs.
“Our new Polaris architecture showcases significant advances in performance, power efficiency and features,” said Lisa Su, president and CEO, AMD. “2016 will be a very exciting year for RadeonT fans driven by our Polaris architecture, Radeon Software Crimson Edition and a host of other innovations in the pipeline from our Radeon Technologies Group.”
The Polaris architecture features AMD’s 4th generation Graphics Core Next (GCN) architecture, a next-generation display engine with support for HDMI® 2.0a and DisplayPort 1.3, and next-generation multimedia features including 4K h.265 encoding and decoding.

AMD compared the power consumption of two Core i7-4790K-based platforms—one with Polaris and another with Nvidia’s desktop GeForce GTX 950—using the Medium quality preset. The system with AMD’s onboard averaged 86 W, whereas the Nvidia’s GTX 950 got about 50 W of system power use.
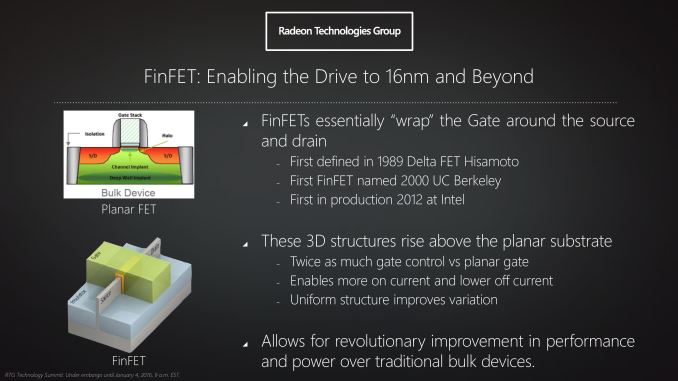
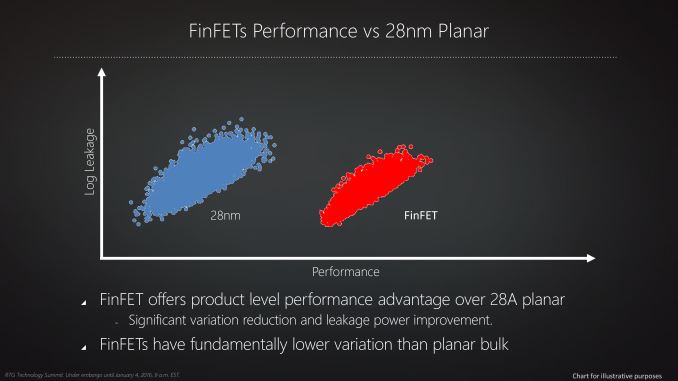
The new architecture has 4th Generation Graphics Core Next Compute Units (aka. GCN 4.0), AMD Polaris will compete against NVIDIA’s Pascal architecture, and both are expected to utilize High-Bandwidth-Memory 2 (HBM2). AMD is expected to release their first 400 series cards in the summers of 2016.